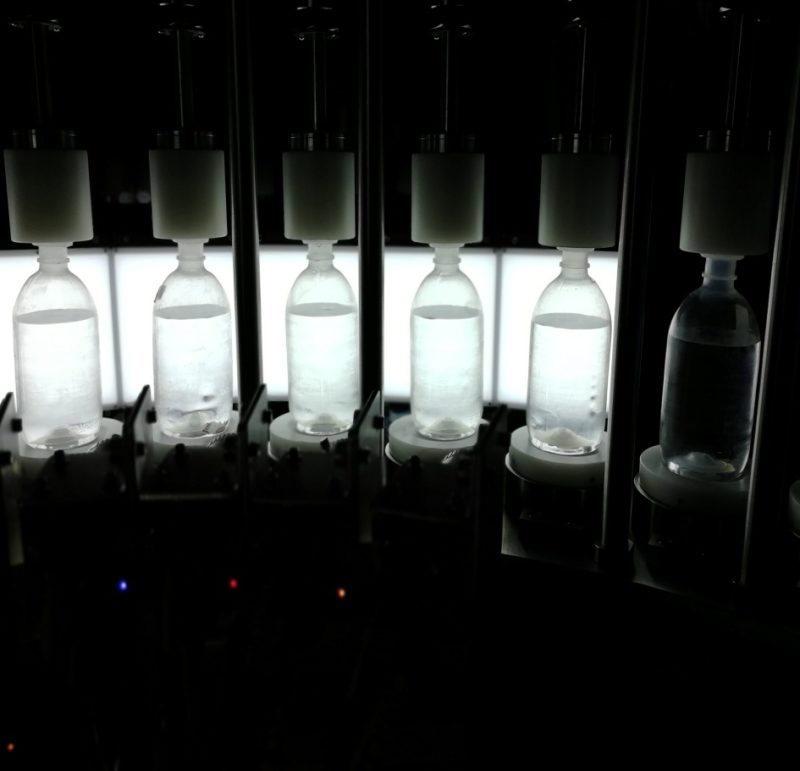
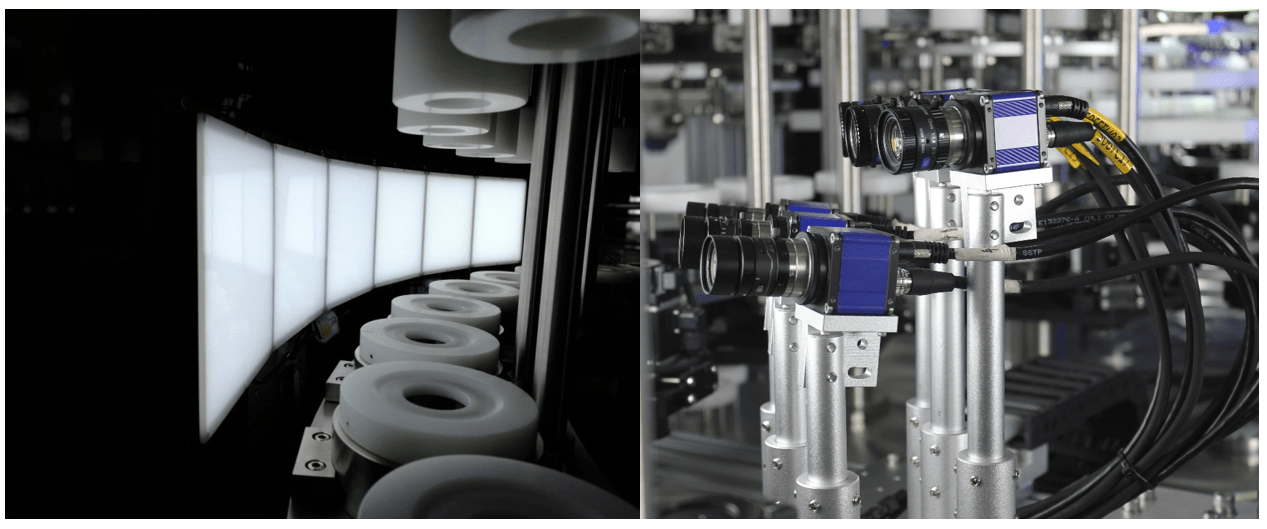
Visual inspection systems for detecting particulates are essential in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, automotive, electronics, and more. These systems utilize advanced imaging technologies and algorithms to identify and analyze particulates in products or processes. Here’s how they typically work:
1. Imaging Technology:
Visual inspection systems use high-resolution cameras or sensors to capture images of the product or process being inspected. These cameras may employ various techniques such as bright-field imaging, dark-field imaging, or fluorescence imaging, depending on the nature of the particulates and the background.
2. Illumination:
Proper lighting is crucial for highlighting particulates against the background. Different illumination techniques, such as diffused lighting or polarized lighting, can enhance contrast and make particulates more visible.
3. Image Processing and Analysis:
Once images are captured, sophisticated image processing algorithms are applied to analyze them. These algorithms can detect and characterize particulates based on various features such as size, shape, color, texture, and intensity.
4. Classification and Sorting:
After detection and analysis, particulates are classified based on predefined criteria. Depending on the application, the system may categorize particulates as acceptable or rejectable. In some cases, automated sorting mechanisms are integrated into the system to remove defective products from the production line.
5. Data Logging and Reporting:
Visual inspection systems typically provide data logging capabilities to record inspection results over time. This data can be used for quality control purposes, process optimization, and regulatory compliance. Additionally, these systems often generate reports summarizing inspection outcomes for documentation and analysis.
6. Integration with Production Line:
To ensure seamless operation, visual inspection systems are often integrated into existing production lines. They may communicate with other equipment and control systems to coordinate inspections with manufacturing processes.
7. Customization and Flexibility:
Visual inspection systems can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different industries and applications. This may involve adjusting parameters such as camera settings, lighting conditions, and image processing algorithms to achieve optimal performance.
8. Maintenance and Calibration:
Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of visual inspection systems. This includes cleaning optics, checking lighting sources, and calibrating image processing algorithms to account for changes in environmental conditions or product characteristics.
Overall
visual inspection systems play a critical role in ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance in diverse industrial settings where the presence of particulates can impact the final product’s integrity.
Visual Inspection Machine For IV PP bottle