I. Introduction
In the intricate world of pharmaceutical manufacturing, every decision holds paramount importance, especially when it concerns patient safety and product integrity. One such critical decision revolves around selecting the appropriate materials for IV solution bottles. This blog post delves into the comparison between two prevalent options: Polypropylene (PP) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) bottles, examining their properties, advantages, disadvantages, safety considerations, environmental impact, cost analysis, and industry insights.
II. Understanding PP and PVC
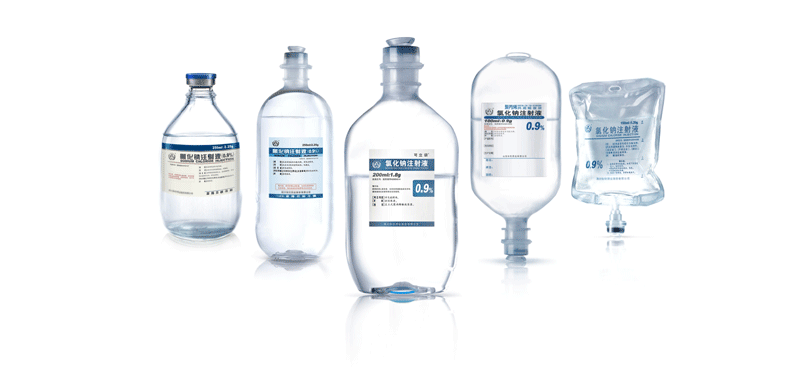
Polypropylene (PP) stands out for its durability, resistance to chemicals, and high melting point, making it a favored choice in various industries, including pharmaceuticals. On the other hand, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) boasts flexibility, transparency, and ease of processing, but raises concerns due to plasticizers used in its production.
III. Advantages and Disadvantages of PP Bottles
PP bottles offer numerous benefits such as chemical inertness, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of medications, and high tensile strength, reducing the risk of breakage during transportation. However, their susceptibility to permeation and potential for leachable compounds may pose challenges.
IV. Advantages and Disadvantages of PVC Bottles
PVC bottles provide excellent barrier properties, preserving the integrity of IV solutions. Their flexibility facilitates handling and reduces the likelihood of breakage. Nevertheless, the use of plasticizers in PVC production raises concerns about leaching and environmental impact.
V. Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Both PP and PVC bottles undergo stringent regulatory scrutiny to ensure compliance with safety standards. While PP is generally considered safer due to its lower risk of leaching harmful substances, PVC requires careful monitoring and adherence to regulatory guidelines to mitigate potential health hazards.
VI. Environmental Impact
Comparing the environmental sustainability of PP and PVC bottles reveals varying degrees of recyclability and eco-friendliness. PP bottles are more readily recyclable and less harmful to the environment during production and disposal compared to PVC, which poses challenges due to its chlorine content and plasticizer use.
VII. Cost Analysis
When evaluating the cost implications, pharmaceutical manufacturers must consider not only the initial purchase price but also long-term savings and overall budget considerations. While PP bottles may initially seem costlier, their durability and compatibility with a wide range of medications can lead to cost savings in the long run.
VIII. Case Studies and Industry Insights
Real-world examples showcase how pharmaceutical companies navigate the decision-making process between PP and PVC bottles based on factors such as product requirements, regulatory compliance, and sustainability goals. Industry experts provide valuable insights into emerging trends and best practices in material selection for IV solution bottles.
IX. Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between PP and PVC bottles for IV solutions involves careful consideration of various factors, including safety, regulatory compliance, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness. While both materials offer unique advantages and challenges, pharmaceutical manufacturers must prioritize patient safety and product quality in their decision-making process. Ultimately, informed decision-making, backed by thorough research and adherence to regulatory guidelines, ensures the optimal selection of materials that meet both industry standards and patient needs.