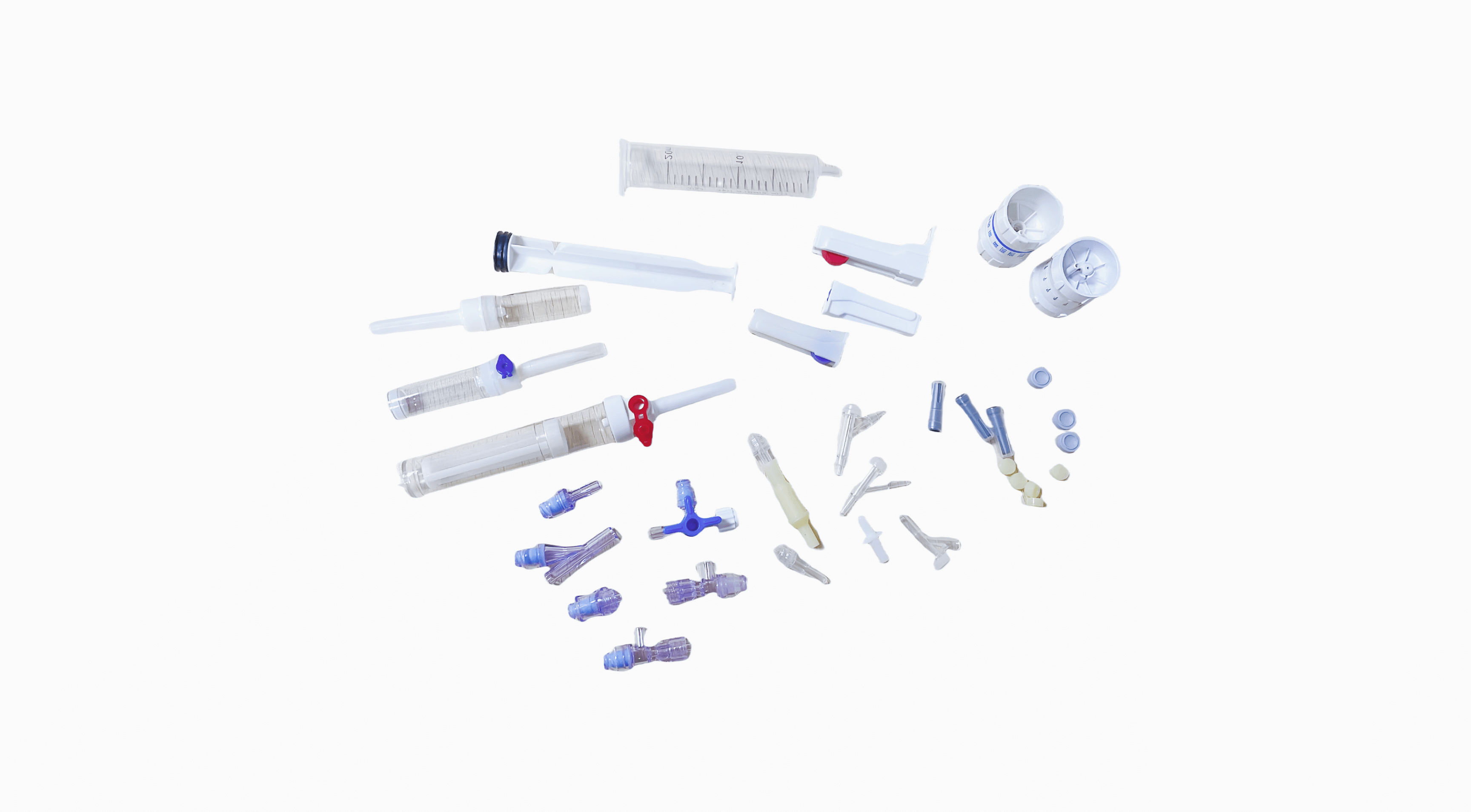
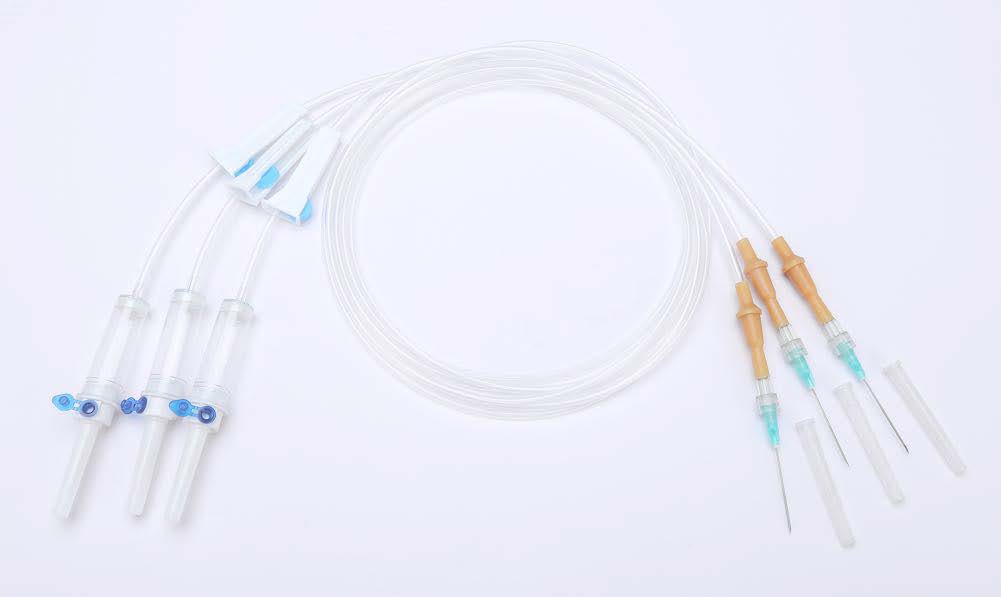
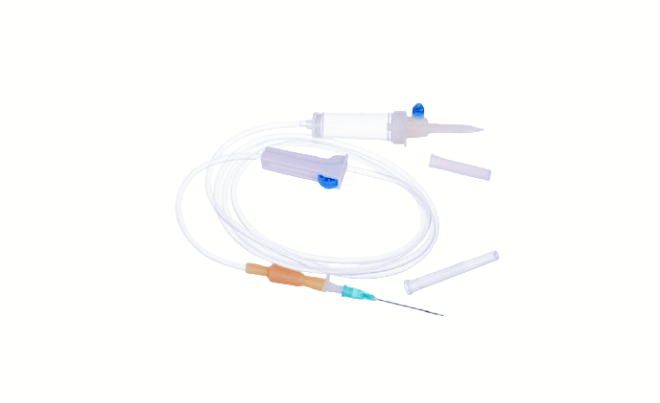
Intravenous (IV) sets consist of several essential components that work together to deliver fluids and medications directly into patients’ veins. Let’s break down these components and understand their roles:
- Tubing: The tubing carries fluids from the IV bag or container to the patient’s vein. It is flexible to allow for easy movement and positioning during treatment.
- Drip Chamber: The drip chamber is where the flow of fluids can be monitored and adjusted. It helps regulate the rate of fluid delivery and allows healthcare professionals to detect any air bubbles or irregularities in the flow.
- IV Connector: The IV connector attaches the IV tubing to the patient’s catheter or needle. It ensures a secure connection and prevents leaks or disconnections during treatment.
- Injection Port: The injection port provides a site for administering medications or additional fluids into the IV line. It allows for easy access without the need to disrupt the primary IV infusion.
- Flow Regulator: The flow regulator is a device for controlling the rate of fluid delivery. It allows healthcare professionals to adjust the flow rate according to the patient’s needs and treatment requirements.
- Needle or Catheter: The needle or catheter is the entry point into the patient’s vein for delivering fluids or medications. It must be inserted correctly and securely to prevent complications such as infiltration or infection.
Understanding the function of each IV set component is essential for proper assembly and administration. Healthcare professionals must ensure that all components are in good condition and properly connected before initiating IV therapy.