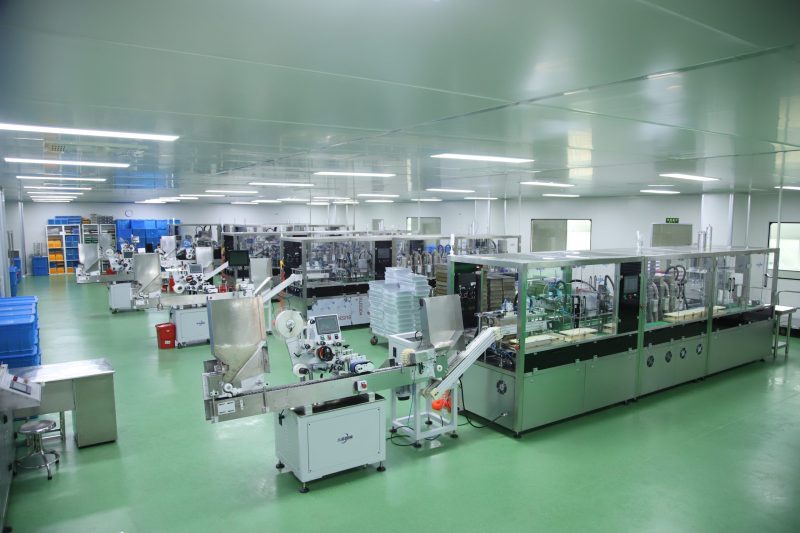
Introduction:
Blood collection tubes are crucial components in healthcare, facilitating various diagnostic procedures. Understanding their manufacturing process sheds light on the intricacies involved in producing these vital medical tools. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the blood collection tube manufacturing process, exploring its stages, materials, and technologies.
Stages of Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing :
1. Material Selection: The manufacturing process begins with careful selection of materials. Primary components include plastic polymers for tube bodies, rubber stoppers, and additives for anticoagulation and preservation.
2. Injection Molding: Injection molding is a pivotal stage where molten plastic is injected into molds to form the tube bodies. Precision and consistency are critical to ensure uniformity in shape and dimensions.
3. Stopper Production: Rubber stoppers are manufactured separately using compression or injection molding techniques. These stoppers must fit snugly into the tube bodies to prevent leakage.
4. Coating Application: To enhance compatibility with blood samples, tubes may undergo coating processes. Silica or other materials are applied to the inner surface to improve clotting and prevent sample adherence.
5. Additive Incorporation: Anticoagulants and preservatives are added to the tubes in precise quantities. This step requires meticulous attention to dosage to ensure proper blood preservation without compromising sample integrity.
6. Sterilization: Once assembled, the tubes undergo sterilization to eliminate microbial contaminants. Sterilization methods may include autoclaving, gamma irradiation, or ethylene oxide treatment.
Materials Used in Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing :
1. Plastic Polymers: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used for tube bodies due to their inertness, transparency, and durability.
2. Rubber: Natural rubber or synthetic elastomers like butyl rubber are employed for stoppers, providing flexibility and airtight sealing properties.
3. Additives: Anticoagulants such as EDTA, heparin, or citrate, and preservatives like sodium fluoride or clot activators, are essential additives to maintain sample quality.
4. Coating Materials: Silica coatings or silicone-based compounds improve tube surface properties, aiding in sample collection and processing.
Technologies in Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing :
1. Injection Molding: Advanced injection molding machines equipped with precise controls ensure consistent tube production.
2. Automated Assembly Lines: Automated assembly lines streamline the manufacturing process, minimizing human error and maximizing efficiency.
3. Quality Control Systems: Incorporation of quality control systems such as vision inspection, dimensional checks, and pressure testing guarantees the integrity of each blood collection tube.
4. Sterilization Technologies: Modern sterilization techniques ensure product safety without compromising material integrity or functionality.
Conclusion :
The blood collection tube manufacturing process is a sophisticated endeavor, demanding precision, quality, and adherence to stringent standards. By comprehending the intricacies involved in producing these essential medical tools, we gain a deeper appreciation for the technology and expertise driving modern healthcare. As advancements continue to evolve, the pursuit of excellence in blood collection tube manufacturing remains paramount, ensuring the reliability and efficacy of diagnostic procedures worldwide.
Blood collection tube line