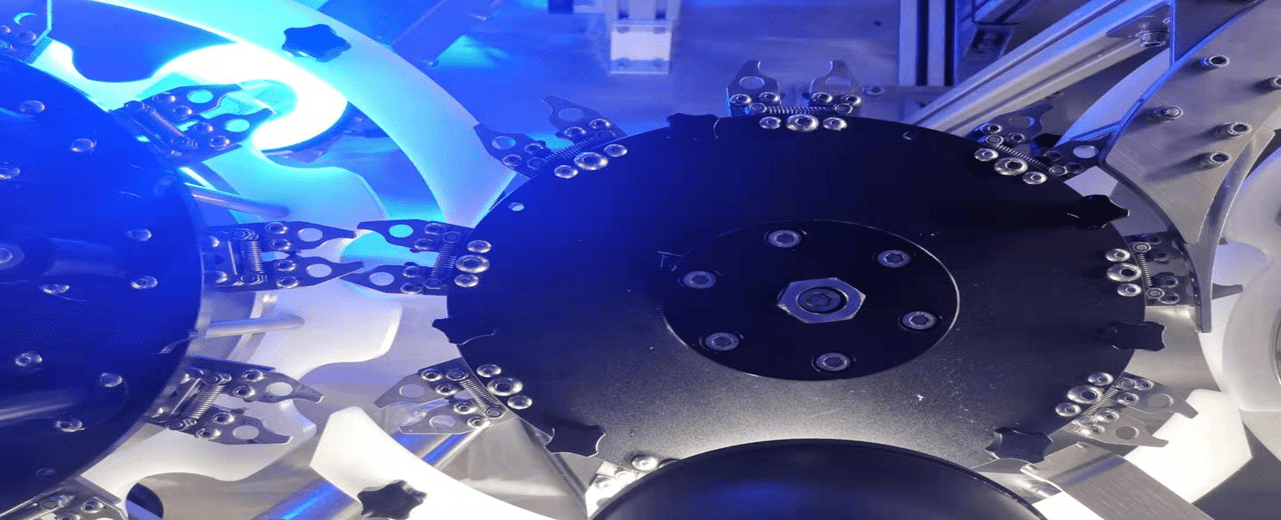
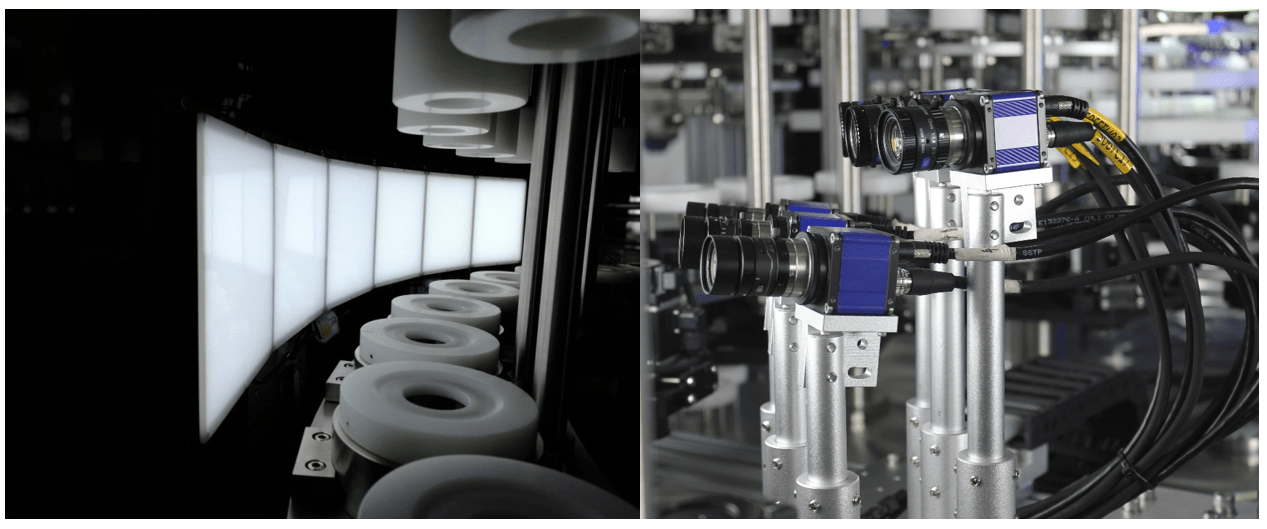
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, precision and quality control are of utmost importance. Every step in the production process demands meticulous attention to detail to ensure the safety and efficacy of the final product. Visual inspection machines emerge as indispensable assets among the myriad of technologies employed, wielding the power to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance within the pharmaceutical industry.
Understanding Visual Inspection Machines
Visual inspection machines are sophisticated instruments that scrutinise pharmaceutical products with unmatched precision. Employing advanced imaging technology, these machines meticulously examine various aspects of a product, ranging from its physical appearance to its structural integrity. By leveraging high-resolution cameras, lighting systems, and image-processing algorithms, they can detect even the minutest imperfections that evade the human eye.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
1. Quality Assurance:
Visual inspection machines are the first defence in ensuring product quality. By scrutinising the visual attributes of pharmaceutical products such as tablets, capsules, and vials, these machines can identify defects such as cracks, chips, discolourations, and contamination. Detecting these anomalies early prevents defective products from reaching consumers, safeguarding public health and brand reputation.
2. Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
Adherence to stringent quality standards is non-negotiable in the highly regulated pharmaceutical industry. Visual inspection machines play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements set forth by authorities such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). By providing objective and consistent assessments, these machines assist manufacturers in meeting the rigorous standards governing pharmaceutical production.
3. Batch Traceability:
Maintaining accurate batch records is essential for tracking and tracing pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle. Visual inspection machines facilitate batch traceability by capturing detailed images of each product inspected, along with relevant metadata such as batch numbers and manufacturing dates. This documentation enables swift identification of defective batches and facilitates investigations in the event of quality-related incidents or recalls.
4. Process Optimisation:
Visual inspection machines contribute to process optimisation by identifying areas for improvement within the manufacturing workflow. Manufacturers can pinpoint recurring defects or inefficiencies by analysing inspection data and implementing corrective measures to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. Moreover, real-time monitoring capabilities allow for immediate intervention in case of deviations from predefined quality parameters, minimising the risk of product defects.
5. Minimising Human Error:
While human inspectors play a vital role in quality control, they are susceptible to fatigue, distraction, and subjectivity. Visual inspection machines mitigate the risk of human error by providing consistent and objective assessments around the clock. By automating repetitive inspection tasks, these machines free up human resources to focus on more complex and value-added activities, thereby improving overall productivity and efficiency.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
The efficacy of visual inspection machines in pharmaceutical manufacturing is further amplified by advancements in technology, including:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
AI-powered algorithms enable visual inspection machines to adapt and learn from experience, enhancing their ability to detect subtle defects and anomalies. By continuously refining their algorithms based on feedback from inspection data, these machines achieve unparalleled accuracy and reliability over time.
2. Hyperspectral Imaging:
Hyperspectral imaging expands the capabilities of visual inspection machines by capturing detailed spectral information beyond the visible spectrum. This enables the detection of anomalies such as counterfeit drugs, impurities, and variations in chemical composition that may not be discernible through conventional visual inspection methods.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
AR and VR technologies offer immersive visualisation tools that empower operators to interact with real-time inspection data. By overlaying digital information onto physical objects, these technologies enhance situational awareness and decision-making capabilities, enabling operators to identify and address issues swiftly during inspection.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of pharmaceutical manufacturing, visual inspection machines emerge as indispensable assets, driving efficiency, quality, and compliance across the production lifecycle. By harnessing the power of advanced imaging technology and data analytics, these machines empower manufacturers to uphold the highest standards of product quality while meeting regulatory requirements and consumer expectations. As the industry continues to evolve, visual inspection machines will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of innovation, safeguarding the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products for generations to come.
Visual Inspection Machine