Introduction:
In the dynamic world of pharmaceutical manufacturing and medical diagnostics, precision and reliability reign supreme. EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) blood collection tubes stand as crucial tools, ensuring accurate and consistent results in laboratory tests. Unraveling the benefits, applications, and best practices linked with EDTA blood collection tubes is pivotal for healthcare professionals and researchers alike. This article delves into the pivotal role of EDTA tubes in blood collection and analysis, shedding light on their profound importance in the pharmaceutical industry.
Understanding EDTA Blood Collection Tubes:
EDTA blood collection tubes, vacuum-sealed containers infused with EDTA as an anticoagulant, are pivotal in maintaining blood samples’ integrity for analysis. By chelating calcium ions, EDTA prevents clot formation, preserving the liquid state of the blood sample. These tubes, available in various sizes and predominantly coded in lavender or purple, stand as indispensable assets in healthcare settings.
Benefits of EDTA Blood Collection Tubes:
Clot Prevention: EDTA’s primary role in blood collection tubes is inhibiting clotting by binding to calcium ions, ensuring the preservation of samples for analysis.
Cell Morphology Preservation: EDTA aids in maintaining blood cell integrity, facilitating accurate examination of cellular components in diagnostic tests like complete blood count (CBC).
Facilitating Molecular Diagnostics: The clot-free nature of EDTA blood samples streamlines molecular diagnostic techniques such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), enabling efficient nucleic acid extraction.
Versatility: EDTA tubes find extensive application across various laboratory procedures, spanning hematology, immunology, and molecular biology, establishing them as indispensable tools in pharmaceutical manufacturing and clinical research.
Applications of EDTA Blood Collection Tubes:
Hematology: EDTA tubes are extensively employed for hematological analyses, including CBC, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and blood film examination.
Blood Banking: EDTA plays a pivotal role in blood banking by preserving whole blood and blood components for transfusion.
Molecular Diagnostics: The anticoagulant properties of EDTA facilitate molecular diagnostic tests such as DNA extraction, PCR, and genetic screening.
Toxicology: EDTA blood samples are utilized in toxicology screenings to analyze drug levels and detect poisoning.
Best Practices for Handling EDTA Blood Collection Tubes:
Thorough Mixing: After blood collection, ensure vigorous mixing of the sample with the anticoagulant to prevent clot formation and ensure homogeneity.
Prompt Processing: Process EDTA blood samples promptly to minimize cellular degradation and maintain sample integrity.
Optimal Storage: Store EDTA tubes at recommended temperatures to preserve sample stability and prevent analyte degradation.
Accurate Labeling and Documentation: Ensure precise labeling of EDTA tubes with patient information and test details for traceability and quality assurance.
In Conclusion:
EDTA blood collection tubes stand as indispensable assets in pharmaceutical manufacturing and medical diagnostics, offering myriad benefits in sample preservation and analysis. Understanding their uses and adhering to best practices is imperative for healthcare professionals and researchers striving for reliable and accurate laboratory results. By integrating these insights into pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, one can optimize the use of EDTA blood collection tubes and elevate the quality of laboratory testing protocols.
Should you have any queries or require further information about EDTA blood collection tubes, feel free to reach out. We’re here to assist you in navigating the intricacies of laboratory sample management and analysis.
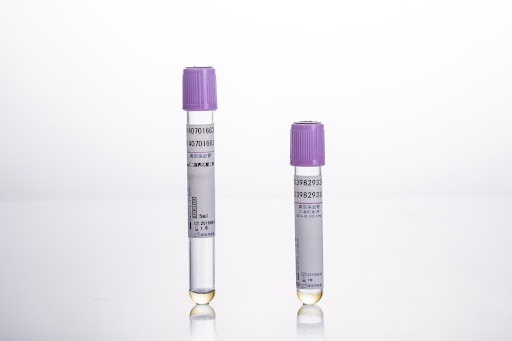
Blood collection tube line